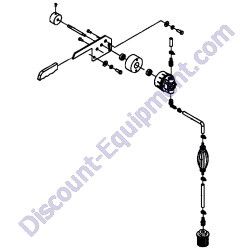
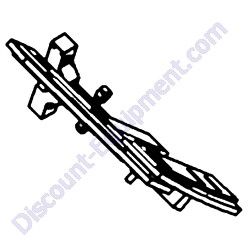
TK CM12-DY7E 12 Cu. Ft. Concrete Mixer With 6.4 HP Yanmar Diesel Electric Start Plus Free Tow Pole
Safety Information
CONCRETE MIXER OSHA REGULATIONS
Construction Safety and Health Outreach Program
U.S. Department of Labor
OSHA Office of Training and Education
May 1996
INTRODUCTION
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration's standard, Subpart Q, Concrete and Masonry Construction, Title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1926.700 through 706, sets forth requirements with which construction employers must comply to protect construction workers from accidents and injuries resulting from the premature removal of formwork, the failure to brace masonry walls, the failure to support precast panels, the inadvertent operation of equipment, and the failure to guard reinforcing steel.
SCOPE AND APPLICATION
The standard, Subpart Q, prescribes performance-oriented requirements designed to help protect all construction workers from the hazards associated with concrete and masonry construction operations at construction, demolition, alteration or repair worksites. Other relevant provisions in both general industry and construction standards (29 CFR Parts 1910 and 1926) also apply to these operations.
Read full article on: https://www.osha.gov/doc/outreachtraining/htmlfiles/concrete.html
PROTECT YOUR BODY
Protect your head and eyes
Protect your body is important while working with concrete, some tips to help you:
Protect Your Head. Wear a hard hat for head protection! Working on a construction site presents a variety of items to avoid that can cause serious head injury. Both construction equipment and tools are frequent potential hazards to concrete contractors and do-it-your-selfers.
Protect Your Eyes. Wear proper eye protection when working with cement or concrete. Splattering concrete and blowing dust can easily enter your eyes during a concrete placement.Wear full cover goggles or safety glasses with side shields, depending on the conditions at your project.
Protect Your Skin. Protect yourself from skin irritation and chemical burns when working with fresh concrete. Severe burns can result with on-going contact between fresh concrete and skin surfaces, eyes, and clothing. Get minor burns treated by a physician, if they persist. Seek immediate medical help if burns affect a large area of your skin or appear to be deep.
Protect Your Skin. Avoid direct skin contact with sand and aggregate since they are very abrasive to your skin. Don't handle wet cement directly since it is basic so it will be injurious to your skin.
Protect Your Skin. Don't handle cement without protection since it will draw moisture from your skin. Wear protective clothing, such as waterproof gloves, long-sleeved shirts, and long pants to keep the concrete from making contact with your skin.
Protect Your Skin. Ensure the protective clothing stays dry so it does not transfer the alkaline or hygroscopic effects to the skin. Wear rubber boots if you must stand in the fresh concrete while it is being placed, screened, or floated to prevent concrete from flowing into them and making contact with your lower legs, ankles and feet.
Protect Your Skin. Use waterproof pads to protect your skin, knees, elbows, or hands from contact with fresh concrete during finishing. Flush eyes and skin that come in contact with fresh concrete immediately with clean water.
Protect Your Skin. Rinse clothing saturated from contact with fresh concrete quickly with fresh water. Wear clean, dry, clothing each work day or for your project. Take a bath or shower at the end of the work day or the conclusion of your do-it-yourself project.
Protect Your Back. Be careful how you move heavy materials. Working with the normal materials that are required to make and pour concrete such as cement, aggregate, sand, and water can be very strenuous to the average person's back. Most of these materials are heavy even in small quantities.
Protect Your Back. Take care to lift properly keeping your back straight and your legs bent to avoid serious back strain. Carry these materials, if you have to, keeping them waist high and centered between your legs to lessen the chance for injury.
Protect Your Back. Use mechanical or manual equipment whenever possible to move materials as close to its final placement area. Use a cement mixer's chute, a concrete pump, or just a wheelbarrow to get the concrete placed. Push the concrete to its final position with a shovel or similar tool. Do not lift the concrete mix.
|